Credibility: the quality of being worthy of belief and trust
Credibility, which flows from character and competence, is one of the most essential aspects of leadership. High credibility is a tremendous asset for leaders seeking to achieve exceptional performance and positive impacts. Low credibility is devastating.
Credible leaders are straight with people, even about hard topics. They walk the talk and practice what they preach. They do what they say they will do and follow through on promises.
Think about what you have wanted from your leaders, parents, teachers, and coaches over the years. Next, think of the impact that credible leaders have had on your life. And think of the kind of leader you would want your children or best friend to work for.
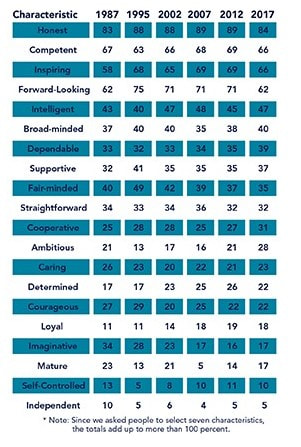
Characteristics of Admired Leaders
Leadership scholars James Kouzes and Barry Posner, authors of the best-selling classic, The Leadership Challenge, have been surveying people around the world for decades on the “Characteristics of Admired Leaders.” More than 100,000 people worldwide have responded, and the findings are powerful and surprisingly consistent across nations:
“In every survey we’ve conducted, honesty is selected more often than any other leadership characteristic. Overall, it emerges as the single most important factor in the leader-constituent relationship…. First and foremost, people want a leader who is honest…. “…people want to follow leaders who, more than anything, are credible. Credibility is the foundation of leadership. People must be able, above all else, to believe in their leaders. To willingly follow them, people must believe that the leaders’ word can be trusted.” -James Kouzes and Barry Posner, The Leadership Challenge
Table 1. Characteristics of Admired Leaders
(% of respondents selecting each characteristic over time periods)
The Benefits of Leadership Credibility
According to their research, when people perceive their manager to have high credibility, they are significantly more likely to:
- Be proud to tell others they’re part of the organization
- Feel a strong sense of team spirit
- See their own personal values as consistent with those of the organization
- Feel attached and committed to the organization
- Have a sense of ownership of the organization
When they perceive their manager to have low credibility, they are significantly more likely to:
- Produce only if carefully watched
- Be motivated primarily by money
- Say good things about the organization publicly but criticize it privately
- Consider looking for another job if the organization experiences problems
- Feel unsupported and unappreciated
That leads them to the Kouzes-Posner 1st Law of Leadership:
“If you don’t believe in the messenger, you won’t believe the message.”
And then to the Kouzes-Posner 2nd Law of Leadership:
DWYSYWD: “Do what you say you will do.”
Today we all face grave challenges, from the pandemic and economic crisis, with all their stresses and pressures, to competitive and technological disruption. Now more than ever we need credible leaders worthy of our belief and trust.
What are you doing to build leadership credibility?
“Credibility is a leader’s currency. With it, he or she is solvent; without it, he or she is bankrupt.”
-John C. Maxwell, leadership author
Tools for You
- Quality of Life Assessment so you can discover your strongest areas and the areas that need work, then act accordingly.
- Traps Test (Common Traps of Living) to help you identify what’s getting in the way of your happiness and quality of life
- Leadership Derailers Assessment to help you identify what’s inhibiting your leadership effectiveness
More Articles from Our Series on Ethical Leadership
- The Root Cause of Ethical Failings
- Leadership and the Ethics Imperative
- The Importance of Integrity in Leadership
- The Importance of Trust in Leadership
- The Problem of Bad Leaders—and Why People Keep Following Them
- 10 Benefits of Credibility in Leadership
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
Gregg Vanourek is a writer, teacher, TEDx speaker, and coach on leadership and personal development. He is co-author of three books, including LIFE Entrepreneurs: Ordinary People Creating Extraordinary Lives (a manifesto for integrating our life and work with purpose, passion, and contribution) and Triple Crown Leadership: Building Excellent, Ethical, and Enduring Organizations (a winner of the International Book Awards). Check out his Best Articles or get his monthly newsletter. If you found value in this article, please forward it to a friend. Every little bit helps!





