These days, you may be feeling anxious or concerned. It’s no wonder, given how much uncertainty and strife we’re seeing regularly.
What’s on your mind? Is it concern about high prices or worry about trade wars? Political polarization and social divides? Immigration concerns? Misinformation and disinformation? Or mass shootings, mental health concerns, social justice issues, climate change? Extreme weather events like wildfires and hurricanes?
Last year, 77% of U.S. adults indicated the future of their nation as a significant source of stress in their lives, and 73% indicated the economy as such. The overall average level of stress among Americans in 2024 was 5 out of 10. Source: American Psychological Association’s Stress in America 2024 poll. (1)
Around the world, people are most concerned about inflation, crime and violence, poverty and social inequality, unemployment, and financial/political corruption, according to the What Worries the World survey 2024. (2)
“Most people today live in relatively constant distress and anxiety.”
-Shirzad Chamine, Positive Intelligence
No doubt, there’s plenty to be concerned about. But is your reaction to things helping in any way, or just making you miserable?
Radical Acceptance
A powerful way to break this downward spiral is through “radical acceptance,” which has been defined as “fully acknowledging reality as it is, without resistance or judgment.”
When practicing this form of acceptance, you focus on what you can control and let go of what you can’t.
“Acceptance means events can make it through you without resistance.”
-Michael Singer, The Untethered Soul: The Journey Beyond Yourself
Accepting reality as it is can prevent you from prolonging emotional reactions that only worsen the situation. By practicing radical acceptance, you can enhance your ability to handle distress. Essentially, you’re preventing your pain from turning into unnecessary suffering.
Of course, it’s easier said than done. Truth be told, it can be very challenging in practice, in part because of the way our brains are wired.
What Acceptance Isn’t
In this context, acceptance isn’t the same as avoidance, complacency, settling, or inaction. It doesn’t mean that you throw up your arms and become passive. And no, you shouldn’t put your head in the sand or fiddle while Rome burns.
In life, action is essential. And you’ll still fight to uphold your values and honor your commitments.
But acceptance means that you’ll stop resisting reality. It means that you’ll focus on having a productive, compassionate, and nonjudgmental mindset. Why? Because it will benefit you and those around you.
Why You Should Practice Acceptance
Practicing acceptance can help you in many ways. For example, it has benefits on your:
- mental and physical health (including your sleep quality and cardiovascular, digestive, and immune systems)
- relationships
- anxiety management
- communication, coping, and problem-solving skills
- conflict management
- performance
- wellbeing
- happiness
“There is something wonderfully bold and liberating about saying yes to our entire imperfect and messy life.”
-Tara Brach, psychologist, author, and meditation teacher
How to Practice Radical Acceptance
How does this work in practice? And how can you apply it, even when things are difficult?
Here are practical steps you can take to practice radical acceptance:
1. Focus on being an observer, not a judge or victim. See things as they are. Stop resisting reality, realizing that it’s futile to do so.
2. Remind yourself that you can’t always change your current reality. And that’s okay. It is what it is.
3. Notice when you’re resisting reality. Common clues include troubling emotions like irritability or resentment. Focus on letting go of that resistance—and your desire for control.
4. Look for patterns or circumstances in which you keep falling into this trap. Pay attention to what you resist and what causes you grief. For example, are you:
- getting triggered by following the news too closely and letting it cloud your days, or by checking your social media accounts too often
- avoiding conflict, hoping it will go away on its own
- getting triggered by someone who annoys you
- unrealistically expecting your boss to change his or her behavior
- resisting responsibility by blaming others
- avoiding the reality that you’re staying in a mediocre or unfulfilling job
- not facing up to your health challenges or ignoring the need for diet and lifestyle changes
5. Live in the present moment. Let go of worries of the past and doubts about the future. Your life is right here, right now. You can’t change the past (although you can change how you view it). And much of what’s to come in the future is beyond your control. That’s okay. Focus on doing your best and acting rightly in the moment. That will set you up for your best chances of success.
6. Practice relaxation techniques such as meditation, deep breathing, or journaling (if it helps you). These practices can help you accept reality as it is with your whole self, including mind, body, and spirit.
7. Allow uncomfortable emotions like frustration, disappointment, and sadness to arise within you. Avoid the temptation to resist or numb them. Doing so will only allow them to linger longer. Emotions are natural and unavoidable. You can’t stop them from arising. They generally last for only about 90 seconds, on average. If you don’t resist them, they’ll pass through you naturally. But if you do resist them, they’ll linger and keep reappearing. According to Dr. Jill Bolte Taylor, a Harvard-trained neuroanatomist and author: (3)
“When a person has a reaction to something in their environment, there’s a 90-second chemical process that happens in the body; after that, any remaining emotional response is just the person choosing to stay in that emotional loop.
Something happens in the external world, and chemicals are flushed through your body which puts it on full alert. For those chemicals to totally flush out of the body, it takes less than 90 seconds. This means that for 90 seconds you can watch the process happening, you can feel it happening, and then you can watch it go away.
After that, if you continue to feel fear, anger, and so on, you need to look at the thoughts that you’re thinking that are re-stimulating the circuitry that is resulting in you having this physiological reaction, over and over again.”
8. Direct your energy and attention to things you can control and what you’re grateful for. Avoid ruminating on what’s upsetting you and negative judgments about yourself and others. Acknowledge what you can’t control, knowing that resisting it will only cause you anxiety or suffering.
9. Reframe negative events. For example, think about all your skills and capabilities in overcoming challenges and all the times you’ve survived difficult things and been resilient. Consider that there may be valuable lessons or opportunities for growth in your adversity. (See my article, “The Power of Reframing to Change Our Outlook.”)
10. When you face challenging situations, focus only on being effective in addressing them. The alternative is being reactive, hurt, or wounded—none of which will help you with anything. To the contrary.
“You can’t control how you feel. But you can always choose how you act.”
-Mel Robbins, The 5 Second Rule
11. Focus on your own mindset and actions. Stop expecting others to change or act according to your wishes or expectations.
“The greatest catalyst for change in a relationship is complete acceptance of your partner as he or she is,
without needing to judge or change them in any way.”
-Eckhart Tolle, The Power of Now
12. Consider whether your expectations are realistic and appropriate. Or are they setting you up for disappointment? For example, if you’re always expecting good things to happen to you, you may be inviting frustration and disappointment, because life always comes with ups and downs.
13. Remember that life can be okay—or even precious and rich—even when you’re feeling pain or discomfort. Try to place your current challenges or concerns in context and maintain perspective.
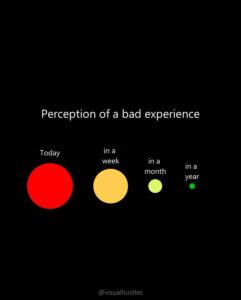
14. Don’t go it alone. Lean on your support system and recall that we’re all in this together.
15. Pray for greater acceptance. Keep the Serenity Prayer close by and refer to it often. Better yet, memorize it. (I have a copy of it hanging on my office wall.) It can help you avoid falling into bad habits and unproductive mindsets.
“God grant me the serenity to accept the things I cannot change,
courage to change the things I can,
and wisdom to know the difference.”
-the “Serenity Prayer”

16. Practice these acceptance techniques over and over again. Acceptance isn’t just a decision. It’s also a mindset and a practice. You want it to become more automatic and habitual, and thus easier over time. Eventually, it will become a part of who you are and how to carry yourself in the world.
In the end, there’s hope, faith, strength, and resilience in this form of acceptance. You can stand in the storm and choose not to spiral down, even when things are hard. And you can soldier on without surrendering your spirit.
Wishing you well with it—and let me know if I can help.
–Gregg

Tools for You
- Traps Test (Common Traps of Living) to help you identify what’s getting in the way of your happiness and quality of life
- Quality of Life Assessment so you can discover your strongest areas and the areas that need work, then act accordingly.
- Leadership Derailers Assessment to help you identify what’s inhibiting your leadership effectiveness
Related Articles & Resources
- “The Powerful Practice of Acceptance”
- “The Incredible Grounding Power of Self-Acceptance”
- “What to Do About Overthinking, Rumination, and Worrying”
- “The Mental Prisons We Build for Ourselves”
- “How to Stop Catastrophizing”
- “On Spirituality and the Good Life“
- Tara Brach, Radical Acceptance: Embracing Your Life With the Heart of a Buddha
- Byron Katie, Loving What Is: Four Questions that Can Change Your Life
- Mel Robbins, The Let Them Theory: A Life-Changing Tool That Millions of People Can’t Stop Talking About
Postscript: Inspirations on Acceptance
- “All the stress that we feel is caused by arguing with what is.” -Byron Katie, Loving What Is: Four Questions that Can Change Your Life
- “The primary cause of unhappiness is never the situation but your thoughts about it. Be aware of the thoughts you are thinking. Separate them from the situation, which is always neutral, which always is as it is…. When you live in complete acceptance of what is, that is the end of all drama in your life.” –Eckhart Tolle, The Power of Now
- “Radical Acceptance is the gateway to healing wounds and spiritual transformation. When we can meet our experience with Radical Acceptance, we discover the wholeness, wisdom and love that are our deepest nature…. The boundary to what we can accept is the boundary to our freedom.” -Tara Brach, psychologist, author, and meditation teacher
- “One of the most amazing things you will ever realize is that the moment in front of you is not bothering you—you are bothering yourself about the moment in front of you.” –Michael Singer, Living Untethered
- “The pain you create now is always some form of nonacceptance, some form of unconscious resistance to what is. On the level of thought, the resistance is some form of judgment. On the emotional level, it is some form of negativity.” -Eckhart Tolle, author and spiritual teacher
- “Life is not the way it’s supposed to be, it’s the way it is. The way you cope with that is what makes the difference.” -Virginia Satir, author, clinical social worker, and psychotherapist
- “Accepting people as they are has the miraculous effect of helping them improve. Acceptance doesn’t prohibit growth; rather, it fosters it.” –Marianne Williamson, spiritual teacher and author
References
(1) The Harris Poll conducted the Stress in America 2024 survey online on behalf of the American Psychological Association in August 2024, with a nationally representative sample of 3,305 U.S. adults ages 18 and older. Also, 41% of U.S. adults reported that the state of the nation has made them consider moving to another country, 32% reported that the political climate has caused strain in their family, and 30% said they limit their time with family due to a difference in values.
(2) Source: The What Worries the World survey involved monthly samples of a panel of more than 20,000 adults in 29 countries. They’ve conducted the survey for more than a decade.
(3) Verduyn, P., & Lavrijsen, S. (2015). Which emotions last longest and why: The role of event importance and rumination. Motivation and Emotion, 39(1), 119–127. “Some emotions last longer than others…. some emotions have been found to persist for a long time whereas others tend to quickly fade away.” The researchers here investigated the duration of emotional experience, distinguishing it from mood. The participants were 233 high school students, with a mean age of 17.02 years. Researchers asked them to complete questionnaires on their experience with several emotions. The researchers noted several limitations of the study, including the possibility of retrospective bias (since students reported emotional episodes from the past) and the fact that it only included high school students.
+++++++++++++++++
Gregg Vanourek is a writer, teacher, and TEDx speaker on personal development and leadership. He is co-author of three books, including LIFE Entrepreneurs: Ordinary People Creating Extraordinary Lives (a manifesto for living with purpose and passion) and Triple Crown Leadership: Building Excellent, Ethical, and Enduring Organizations (a winner of the International Book Awards). Check out his Best Articles or get his monthly newsletter. If you found value in this article, please forward it to a friend. Every little bit helps!