What leads to happiness? We all want to be happy—and for those we care about to be happy.
Here’s the problem: we’re unclear and often badly mistaken about what will bring us happiness.
We’re inundated with messages from family, friends, ads, and social media about what will make us happy. Most of these messages are wrong.
The result:
What we think will make us happy is different from what actually makes us happy.
What Is Happiness?
To understand what’s going on here, we should back up and clarify what we’re talking about. What is happiness?
Turns out it’s not so simple to define. Why? It’s complex, and there are many related factors: wellbeing (a good condition of existence with health, happiness, and prosperity), life satisfaction (how we feel about our lives overall and our future), pleasure, and more.
There are even different types of happiness:
- Hedonic happiness: happiness achieved through experiences of pleasure and enjoyment
- Eudaimonic happiness: happiness through virtuous action, habits of moral excellence, and a full flourishing of self in the world.
My favorite definition of happiness (because it’s so comprehensive) comes from University of California, Riverside psychologist and happiness researcher Sonja Lyubomirsky:
Happiness: “the experience of joy, contentment, or positive well-being, combined with a sense that one’s life is good, meaningful, and worthwhile.”
Don’t stop there, though. Decide for yourself what happiness is for you. And then turn your attention to the next step: what leads to it?
Determinants of Happiness: What Leads to Happiness
The question of what leads to happiness presumes that we have agency over it. That’s actually the source of some debate.
Enter “happiness set-point theory,” the notion that our happiness level is determined primarily by our genes and personality traits. According to this theory, our happiness remains relatively constant throughout our lives. We inevitably return to a relatively stable “happiness set point,” regardless of circumstances. (Note also the related notion of hedonic adaptation, in which we become rapidly accustomed to changes in our circumstances and then settle into that new baseline as if nothing had occurred.)![]()
Many researchers have questioned this happiness set-point theory. Some have noted that it really speaks to a fixed range of potential happiness and wellbeing, not a single set point.
Sustainable Happiness Model
In their prominent article, researchers Sonja Lyubomirsky, Kennon Sheldon, and David Schkade developed the “sustainable happiness model” (SHM), which posits that we have more agency over our happiness levels. They noted that happiness is “governed by three major factors: a genetically determined set point for happiness, happiness-relevant circumstantial factors, and happiness-relevant activities and practices.”
They went on to give preliminary estimates for the “approximate percentage of the variance that each of the three factors accounts for in cross-sectional well-being, as suggested by past research”:
- genetics account for about 50% of the population variance in happiness
- circumstances account for about 10%
- activities and practices account for about 40%
This “happiness pie chart,” as it was dubbed, had important implications:
“Thus the key to happiness lies not in changing our genetic makeup (which is impossible) and not in changing our circumstances (i.e., seeking wealth or attractiveness or better colleagues, which is usually impractical), but in our daily intentional activities.” -Sonja Lyubomirsky, Professor of Psychology, University of California, Riverside
This was encouraging for those of us seeking to influence our happiness (which is, well, all of us).
Revisiting the Data
But then the plot thickened. Some researchers critiqued the paper. In response, two of the original researchers, Lyubomirsky and Sheldon, revisited the “happiness pie chart” in a response via a 2019 follow-up paper. (1)
They stood by their main findings but recognized that the 40% estimate for activities may have been an overestimate and noted some important nuances. First, the three factors mentioned (genes, circumstances, and activities) aren’t isolated factors. Clearly, they influence each other. For example, our genes can influence our tendency to engage in certain activities, like exercise, that influence our happiness. And our circumstances and activities can influence whether genes are expressed, depending on the context of our lives.
Also, the percentages given were preliminary estimates—never meant to represent precise numbers for individuals but rather how much of the differences in happiness among people generally come from different sources. Individual results and factors will vary. “Like all pie charts,” Lyubomirsky noted, “ours was a gross oversimplification.”
But let’s not lose the forest for the trees. Here’s the bottom line:
“Although the pie chart part may have outlived its usefulness, we stand behind the central premise of the SHM, and the supportive research it spawned. Happiness can be successfully pursued, but it is not ‘easy.’”
-Kennon Sheldon and Sonja Lyubomirsky in their 2019 follow-up article
It shouldn’t surprise us that there are nuances, given the complexity of happiness and all its influences. So how does this speak to how we should live?
Different Types of Lives
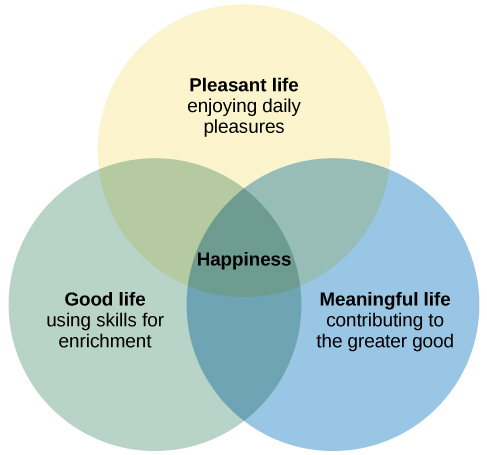
In his book, Authentic Happiness, influential psychologist Dr. Martin Seligman notes different types of lives we can aspire to:
- The pleasant life: the successful pursuit of positive feelings
- The good life: using our “signature strengths”—those character strengths (like courage, diligence, and teamwork, with each person having their own unique set) that are most essential to who we are—to obtain “abundant and authentic gratification,” which comes when we invoke our strengths and virtues, as when we achieve “flow.”
- The meaningful life: using our strengths to serve a larger purpose, such as raising our children, contributing to our community, or fighting for an important cause.
Most of Western society is organized around pursuing the pleasant life. But of the three, Seligman reports, pleasure is the most fleeting.
“For centuries, traditional wisdom has been that simply seeking pleasure for its own sake
doesn’t really make you happy in the long run.”
-Roy Baumeister, Professor of Psychology, Florida State University
Seligman notes that to live all three types of lives—pleasant, good, and meaningful—is to lead a “full life,” which he describes as “experiencing positive emotions about the past and future, savoring positive feelings from the pleasures, deriving abundant gratification from your signature strengths, and using these strengths in the service of something larger to obtain meaning.”
Helpful stuff. But we’re still back to the question: What leads to happiness (and a full life)?
What Leads to Happiness? Actions that Boost Happiness

According to an ever-growing body of research, there are many things we can do to bring happiness to our lives—and to increase our sense of life satisfaction. Here are 20 effective ones:
- Regular exercise and physical activity: moving our bodies regularly, ideally with some vigor. Since our mind and body are connected, our physical activity can have powerful effects on our moods. Exercise has several spillover benefits:
-
- helping us unplug from our devices
- getting us outside more
- helping us sleep better, which is essential for everything we do
- releasing endorphins, which give us pleasure
- reducing anxiety and stress
- giving us feelings of mastery or motivation, and sometimes getting us into a state of flow
- Acts of kindness, caring, service, and generosity: caring for others can help us be happier and healthier, as long as we also engage in self-care and don’t overcommit, burn ourselves out, or care so much that we get lost in the problems or despair of others.
- Purpose and meaning: having a sense of why we’re here and what gives us a sense of deeper significance and connection with something larger than ourselves. This doesn’t have to be grand or complicated. It can begin with worthy activities: engaging in activities that feel meaningful and based on virtues like character and generosity. When we show up as a good person living purposefully—serving others, forgiving people, giving back, being grateful for what we have, and contributing to something larger than ourselves—we end up feeling happier and more fulfilled. It can be parenting or grandparenting—or volunteering, mentoring, or day-to-day acts of service. And it can entail meaningful work, community building, religious worship, or spiritual connection and growth.
- Relationships with others: connecting with others helps us feel love. It gives us a sense of meaning, self-worth, significance, and belonging. It also means we’re more likely to receive support when we need it most. And to provide it when others need it most. According to many researchers, strong social relationships are the most important contributor to enduring happiness for most people. Those who are happiest generally devote a great amount of time to their family and friends. They nurture and enjoy those relationships.
- Goals and Aspirations: having a deep commitment to lifelong goals and ambitions (like parents teaching children their values), ideally “self-concordant goals” (ones that are intrinsically interesting and congruent with our identity). This gives us things to work toward and look forward to. It’s highly motivating, especially with intrinsic aspirations, not extrinsic ones (where the motivation is to seek rewards or avoid punishments). Note: Goals should be challenging, but not too challenging (lest we get deflated for failing to achieve unrealistic goals).
- Authentic expression of self: being true to who we really are and avoiding the traps of wearing a mask, people pleasing, or caring too much about what others think.
- Anticipation: having something to look forward to (e.g., a vacation, date nights, wedding).
“We need the sweet pain of anticipation to tell us we are really alive.”
-Albert Camus, French philosopher
- Gratitude: being thankful for what we have can have powerful effects on our quality of life, including improved wellbeing, life satisfaction, sense of connectedness, and health. Activities such as daily gratitude journaling or writing gratitude letters to those who’ve helped us can have surprisingly strong and lasting effects.
- Experiences: enjoying encounters and activities that are engaging and fun. Tip: consider spending money more on activities (e.g., live shows or social dinners), not so much on things (clothes or gadgets).
- Learning and developing: learning new things and boosting our skills and capacities engages our curiosity, challenges us, helps our brains make connections across domains, and gives us a sense of confidence and accomplishment.
- Meditation and mindfulness practices: activities that help us experience focused attention and achieve a heightened state of awareness can contribute significantly to our happiness and wellbeing. This includes stopping and noticing what’s going on around and within us. It helps us get in touch with our feelings and experience them (which is much better than avoiding or suppressing them, which can be toxic). And it helps us focus on the present instead of dwelling on the past or worrying about the future.
- “Person-activity fit”: engaging in activities that feel enjoyable and natural to us, and that are aligned with our personality, goals, interests, and values. It also means not doing things out of guilt or due to outside pressures or expectations.
- Seeing the positive and reframing the negative: look for the good in things and practice optimism when imagining our future. According to researchers, humans have a negativity bias—over-focusing on negatives and underappreciating positives. It’s important to reframe things from setbacks or defeats to challenges or opportunities (e.g., for learning and growth).
- Journaling: Research has shown that writing about stressful experiences can help us create meaning from them. (The same can be true for talking through our feelings with others.)
- Resilience in the face of adversity: invoking our ability to withstand challenges and bounce back from difficult events, showing poise and strength in the process. Since suffering is part of life, we must learn how to deal with it—and ideally grow and learn in the process.
- Savoring: fully feeling and enjoying positive experiences, thereby extending them. Living in the present moment and appreciating what we have.
- Self-care: taking actions to preserve or improve our health and wellbeing, including during periods of stress. We neglect this at our peril, as it’s foundational to the other things.
- Strengths: knowing and doing the things that we’re good at, including knowledge, talents, and skills. Ideally, we design our lives and work around them, as opposed to harping on our weaknesses. And we work with others who have different strengths.
- Intentional and effective use of time: intentional planning and deployment of our time, such that our actual use of time approaches our ideal use of time. How much of our precious time are we wasting?
“Unless a person takes charge of them, both work and free time are likely to be disappointing.”
-Mihaly Csikszentmihalyi, Hungarian-American psychologist
- Variety: mixing things up and breaking old patterns. Even with good things that we enjoy, we can fall into ruts and lose motivation. Our brains enjoy new stimuli. As the saying goes, “Variety is the spice of life.”
“…the pursuit of happiness requires selecting self-appropriate and eudaimonic-type activities (rather than chasing after positive emotions directly); investing sustained (rather than desultory) effort in those activities; and also, practicing them in a varied and changing manner (rather than doing them the same way each time). By such means, people can create for themselves a steady inflow of engaging, satisfying, connecting, and uplifting positive experiences, thereby increasing the likelihood that they remain in the upper range of their happiness potentials.”
-Kennon Sheldon and Sonja Lyubomirsky
Here’s the good news: there’s much we can do to boost our happiness and wellbeing. The point isn’t that we have to do all of these happiness-generating activities. Why not try some new ones? And why not design your days more intentionally?
In the end, our happiness is up to us. What leads to happiness for you?
Tools for You
- Traps Test (Common Traps of Living) to help you identify what’s getting in the way of your happiness and quality of life
- Quality of Life Assessment so you can discover your strongest areas and the areas that need work, then act accordingly
- Personal Values Exercise to help you clarify what’s most important to you
More Articles in this Happiness Series
- Why Happiness Is the Wrong Goal
- The Most Important Contributor to Happiness
- The Most Common Myths about Happiness
- The Surprising Relationship between Success and Happiness
- Why Is Happiness So Elusive?
- The Power of Relationships in Our Lives
- Is This It? On the Disappointment of Success
Postscript: Relevant Theories
- Eudaimonic Activity Model: suggests that engaging in growth-promoting (eudaimonic) goals and intentional behaviors helps people satisfy their basic psychological needs, which results in elevated happiness and wellbeing.
- Hedonic Adaptation Prevention (HAP) Model: describes the different ways we tend to become rapidly accustomed to changes in our circumstances and settle into our happiness baseline as if nothing had occurred. (Sheldon & Lyubomirsky, 2012)
- Sustainable Happiness Model (SHM): a framework for research on how to boost and maintain happiness over time via intentional behaviors and other interventions.
(1) Kennon M. Sheldon & Sonja Lyubomirsky (2019): Revisiting the Sustainable Happiness Model and Pie Chart: Can Happiness Be Successfully Pursued?, The Journal of Positive Psychology.
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
Gregg Vanourek is a writer, teacher, TEDx speaker, and coach on personal development and leadership. He is co-author of three books, including LIFE Entrepreneurs: Ordinary People Creating Extraordinary Lives (a manifesto for living with purpose and passion) and Triple Crown Leadership: Building Excellent, Ethical, and Enduring Organizations (a winner of the International Book Awards). Check out his Best Articles or get his monthly newsletter. If you found value in this article, please forward it to a friend. Every little bit helps!